Diversité spécifique
Glossaries
| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
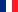
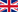
| Diversité spécifique | ♦ La diversité spécifique prend en compte l'abondance relative et le nombre d'espèces. Elle peut se mesurer avec différents indices. > Indice probabiliste de Simpson : Is = 1 / Σpi² où pi = ni / N avec N : somme des S espèces constituant le peuplement considéré > Indice H' de Shannon : H' = - Σpi log2pi Sa valeur varie de (une seule espèce) à log S quand toutes les espèces ont la même abondance. Indice d'équitabilité Il permet de définir l'équirépartition entre les S espèces présentes : E = H‟ / logS Es= Is -1 / S - 1 L'équitabilité varie de à 1. Elle tend vers 0 quand la quasi-totalité des effectifs est concentrée sur une espèce. Elle est de 1 lorsque toutes les espèces ont la même abondance. |